Leaping into the Future of Sustainability with Digital Twins
Posted on : September 6th 2024
Author : Sudhakaran Jampala
A Mirror of Our Times
Digital twins – virtual representations of real-world objects or systems – are pivotal in advancing the Fourth Industrial Revolution. These models, powered by constant real-time data and feedback loops, serve as highly accurate virtual replicas of physical entities.
By digitally mirroring real-world ecosystems, digital twins can accurately simulate the potential impact of various changes or additions. According to the TCS Digital Twindex report (2023), digital twins will become commonplace across business and society by 2035.
Regarding sustainability, the same TCS report states, “Digital twins can model and predict the impacts of various environmental factors and human activities, allowing for more informed decision-making about resource use, emissions reduction, and climate change mitigation strategies.”
The emergence of socially conscious consumers and the growing emphasis on ESG goals make digital twin technology an attractive option for sustainability initiatives. It offers the ability to achieve more with less across multiple domains, including engineering, design, and maintenance. Digital twins are truly reflective of our times.
Critical Use Cases in Sustainability
A critical use case for digital twins is enhancing process efficiencies to reduce emissions or waste in several industrial settings, such as manufacturing.
Mitigating climate change by optimizing energy usage or managing devices with renewable energy sources are other notable examples. Exhibit 1 highlights some of these possibilities.
Exhibit 1: Possibilities for Digital Twins in Sustainability
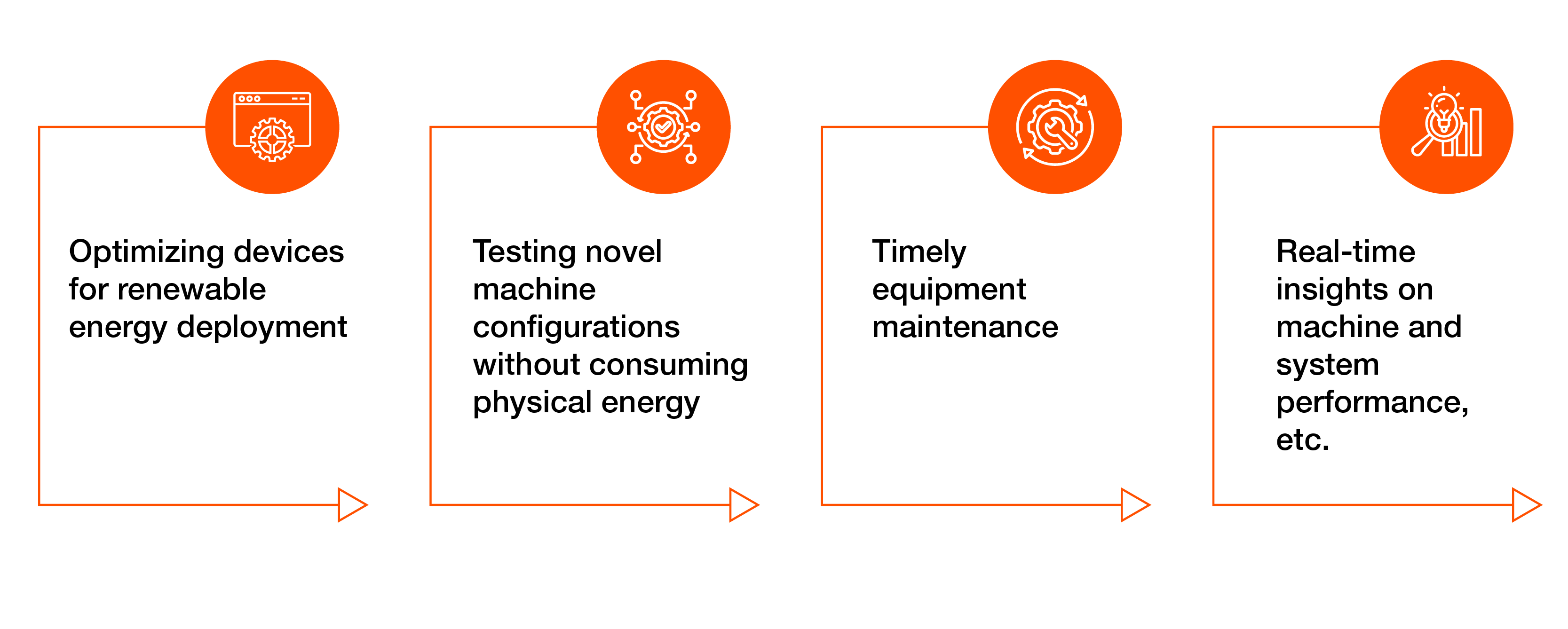
The potential of digital twins in sustainability is only expanding. Latest advances in high-performance computing, sophisticated data analytics, AI/ML, and modern planetary system observations are enhancing the precision of digital representations of physical systems.
As a result, digital twins provide deep insights into the functioning of real-world objects, enabling predictions about various behavioral scenarios of simulated systems. Another significant use case is in the construction industry, where smart buildings are becoming a reality (Exhibit 2).
Exhibit 2: Smart Buildings and Digital Twins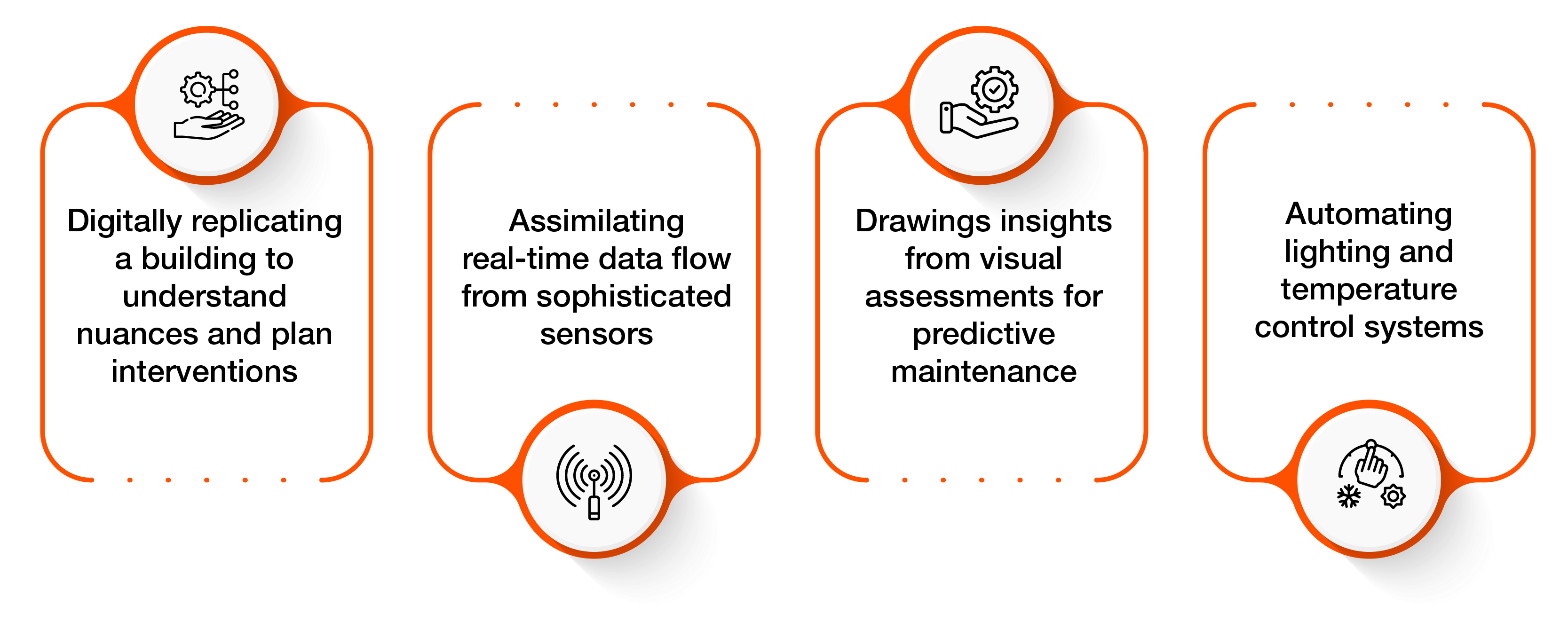
Digital twins drive sustainability efforts by continuously monitoring systemic interactions and providing early warnings when interventions are necessary. The supply chain space, too, is also witnessing a surge in digital twin applications.
For instance, digital twins monitor inventory levels in real time, ensuring companies produce and store only optimal amounts of goods. This minimizes overproduction and reduces the burden of dealing with or disposing of excess goods, positively impacting the environment. In summary, digital twins empower real-time monitoring and dynamic analytics, advancing sustainability goals and strengthening systemic resilience.
Types of Digital Twins
According to McKinsey, there are different types of digital twins (Exhibit 3).
Exhibit 3: Types of Digital Twins
| Type | Brief Description |
| Product twin | Represents a product at different stages of its life cycle. |
| Data twin | For example, Google Maps, which links real-time traffic data to optimize commutes. |
| Systems twin | Models interactions between physical and digital processes, such as manufacturing |
| Infrastructure twin | Represents physical infrastructure like highways or factories. |
Source: McKinsey, Straive Research
McKinsey analysis also projects that the global market for digital-twin technology will grow by about 60 percent annually, reaching $73.5 billion by 2027.
The Future Foretold
Digital twins are key to shaping the future, enabling stakeholders to collaborate effectively and share data proactively. The World Economic Forum highlights four critical areas where digital twins optimize performance for enterprises.
- Production: Identify bottlenecks and predict maintenance needs.
- Waste: Gain real-time insights into material usage and energy consumption.
- Profits: Make data-driven decisions to uncover hidden potential.
- Emissions: Monitor and minimize emissions in real-time.
The development and deployment of digital twins across industries represent a significant leap forward in sustainability. Greener and more efficient industrial ecosystems that foster collaboration across silos offer a win-win for both businesses and the planet.
We want to hear from you
Leave a Message
Our solutioning team is eager to know about your
challenge and how we can help.